When Should Parents in Layton Consider Feeding Therapy for Their Child?
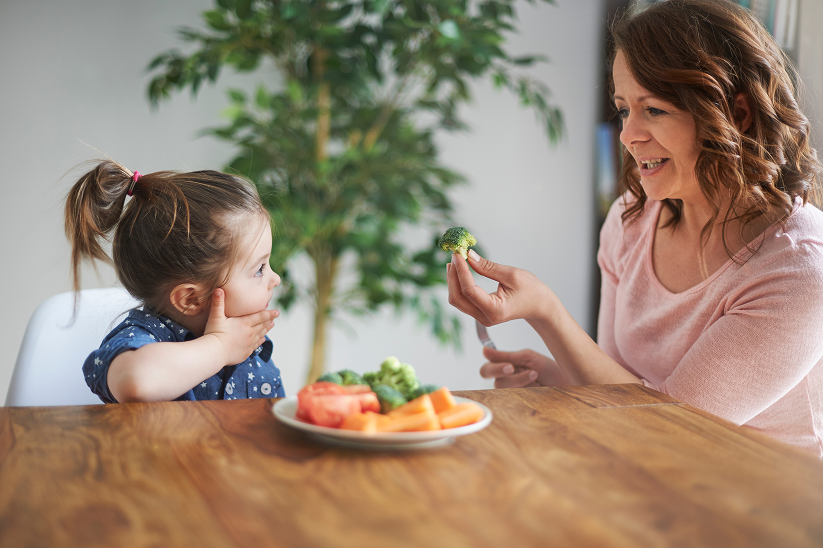
Mealtimes are often expected to be moments of connection, but for many families in Layton, they can feel stressful and confusing. Some children struggle with textures, refuse entire food groups, gag easily, or take an unusually long time to eat. These challenges may go beyond typical picky habits and signal the need for feeding therapy for children. Feeding concerns can affect a child’s growth, daily routine, and family life. Knowing when to seek pediatric feeding therapy helps parents act early and support healthier eating patterns. At Autism Centers of Utah in Layton, families often ask when feeding therapy is the right next step. This guide walks through common signs, causes, and what parents in Layton should consider when deciding on feeding therapy.
What Is Feeding Therapy for Children?
Feeding therapy for children is a supportive service that focuses on helping kids learn how to eat a wider range of foods safely and comfortably. Pediatric feeding therapy addresses challenges such as difficulty chewing, swallowing concerns, sensory sensitivities, and behavioral struggles around food. It is often used for children with developmental delays, autism, oral motor difficulties, or strong food aversions. Feeding therapy Layton services often involve speech or occupational therapy methods that guide children step by step through positive eating experiences. The goal is to help children feel more comfortable with food while supporting nutrition and daily routines.
Common Reasons Children Struggle With Eating
Children can have feeding challenges for many reasons. Some have sensory sensitivities and find certain textures or smells overwhelming. Others may have oral motor delays that make chewing and swallowing difficult. Medical histories such as reflux, premature birth, or tube feeding can also affect eating habits. For children with autism, feeding challenges are common and may include rigid food preferences or anxiety around new foods. These difficulties can appear early or develop over time, which is why parents in Layton often seek pediatric feeding therapy when progress feels stalled.
Signs Child Needs Feeding Therapy
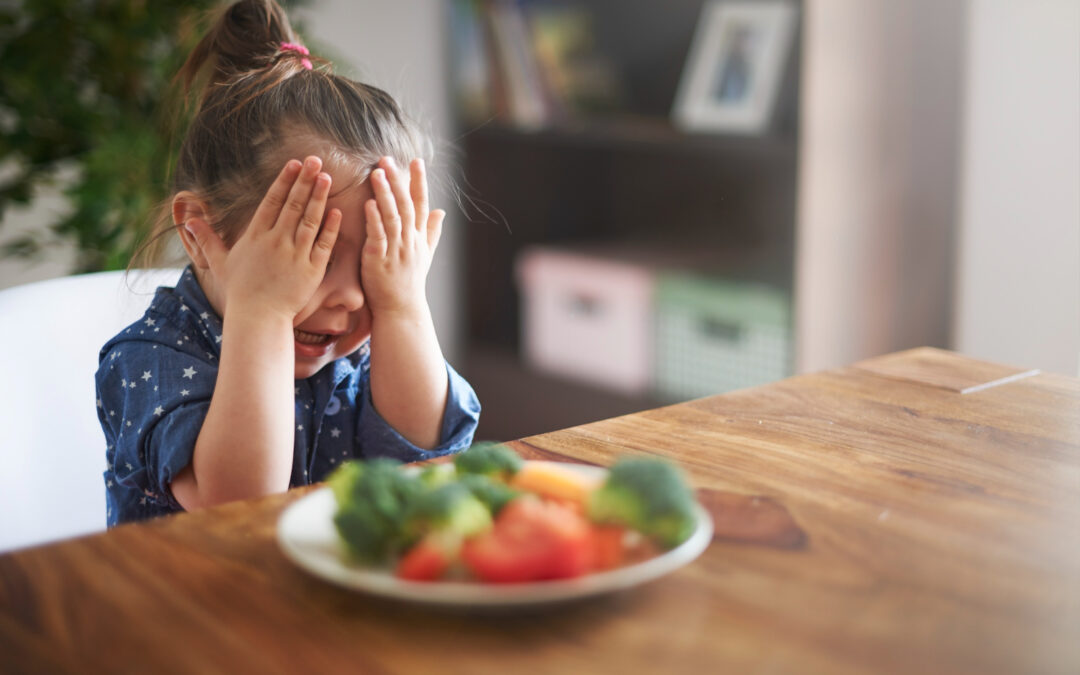
Recognizing early signs can help families avoid ongoing stress at mealtimes. Signs child needs feeding therapy may include eating fewer than ten foods, refusing foods based on color or texture, gagging or vomiting during meals, or extreme distress when new foods are presented. Other signs include difficulty chewing age-appropriate foods, prolonged mealtimes, reliance on specific brands, or avoiding entire food groups. Poor weight gain or frequent choking episodes are also red flags. If these behaviors persist beyond toddler years, feeding therapy for children may be worth exploring.
Picky Eating vs Feeding Disorders
Many parents wonder whether their child is just a picky eater or needs picky eating therapy. Typical picky eating usually improves with age and does not affect growth or health. Feeding disorders, however, are more intense and long-lasting. Children with feeding disorders may have strong emotional reactions to food, limited diets that impact nutrition, or physical difficulty managing food. Pediatric feeding therapy helps identify whether behaviors are developmental or require structured support. In Layton, parents often seek clarity when picky eating begins to interfere with daily life or family routines.
How Feeding Therapy Supports Child Development
Eating is tied closely to development. Feeding therapy for children helps build oral motor skills, sensory tolerance, and positive associations with food. Therapy sessions may include play-based exposure to foods, gradual texture changes, and routines that support calm meals. Pediatric feeding therapy can also reduce stress for parents by offering clear strategies to use at home. Over time, children may become more open to trying foods and participating in family meals. Feeding therapy Layton services focus on progress at a pace that feels manageable for the child and family.
Feeding Therapy and Autism Support
Children on the autism spectrum often experience feeding challenges due to sensory sensitivities and rigid routines. At Autism Centers of Utah, feeding therapy for children is often part of a broader support plan. Feeding therapy can work alongside other services such as aba therapy west jordan utah for families seeking coordinated care across locations. Addressing feeding issues can support overall daily functioning and comfort for children with autism. Early support may help prevent long-term feeding difficulties.
When Parents in Layton Should Seek an Evaluation
Parents in Layton may consider feeding therapy when mealtimes consistently feel stressful or when a child’s diet becomes increasingly limited. If growth concerns arise or if a child avoids eating with others, pediatric feeding therapy can help identify next steps. It is also helpful to seek guidance if feeding challenges affect school participation or social activities. Feeding therapy Layton providers often recommend starting with an evaluation to understand the root causes and outline goals that fit the child’s needs.
What to Expect During Pediatric Feeding Therapy
During pediatric feeding therapy, therapists observe how a child eats, interacts with food, and responds to different textures. Sessions are usually structured yet child-friendly, using encouragement and gradual exposure. Parents are often involved so strategies can be practiced at home. Feeding therapy for children focuses on building trust and reducing anxiety around food. Progress may be gradual, but consistent support helps children feel safer and more confident during meals.
Supporting Feeding Progress at Home
Parents play a key role in feeding therapy success. Creating predictable meal routines, offering a variety of foods without pressure, and modeling calm eating behaviors can support therapy goals. Avoid forcing or bargaining, as these approaches may increase stress. Pediatric feeding therapy often includes guidance for parents to help continue progress between sessions. Families in Layton find that small, steady changes can lead to meaningful improvements over time.
Choosing Feeding Therapy in Layton
When seeking feeding therapy Layton families often look for providers familiar with developmental and sensory needs. Autism Centers of Utah in Layton supports children with feeding challenges as part of a broader care approach. Families appreciate having access to services that understand autism, sensory processing, and behavior patterns related to feeding. Coordinated care helps families feel supported throughout the process.
Long-Term Impact of Early Feeding Support
Early feeding therapy for children can support healthier eating patterns as kids grow. Addressing challenges early may reduce stress around meals, support growth, and help children participate more fully in family and social activities. Pediatric feeding therapy can also build skills that carry into school years and beyond. For many Layton families, feeding therapy offers reassurance and practical tools during a challenging phase.
Final Thoughts for Layton Parents
If you are wondering whether feeding therapy is right for your child, trust your instincts. Ongoing feeding struggles are not something families have to navigate alone. Feeding therapy for children provides guidance, structure, and encouragement for both kids and parents. Autism Centers of Utah in Layton supports families through every step of the process, helping children move toward more comfortable and positive mealtimes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What age can a child start feeding therapy?
Feeding therapy for children can begin in infancy or toddlerhood if feeding concerns are present. Early support is often helpful.
Is picky eating therapy only for autism?
No, picky eating therapy supports children with and without autism who have strong food aversions or limited diets.
How long does pediatric feeding therapy last?
The length of pediatric feeding therapy varies based on the child’s needs and progress. Some children attend for months, others longer.
Can feeding therapy help with gagging or choking?
Yes, feeding therapy Layton services often address gagging, choking, and difficulty chewing through skill-building and gradual exposure.
Do parents participate in feeding therapy sessions?
Yes, parents are usually involved so strategies can be practiced at home and progress can continue outside of sessions.